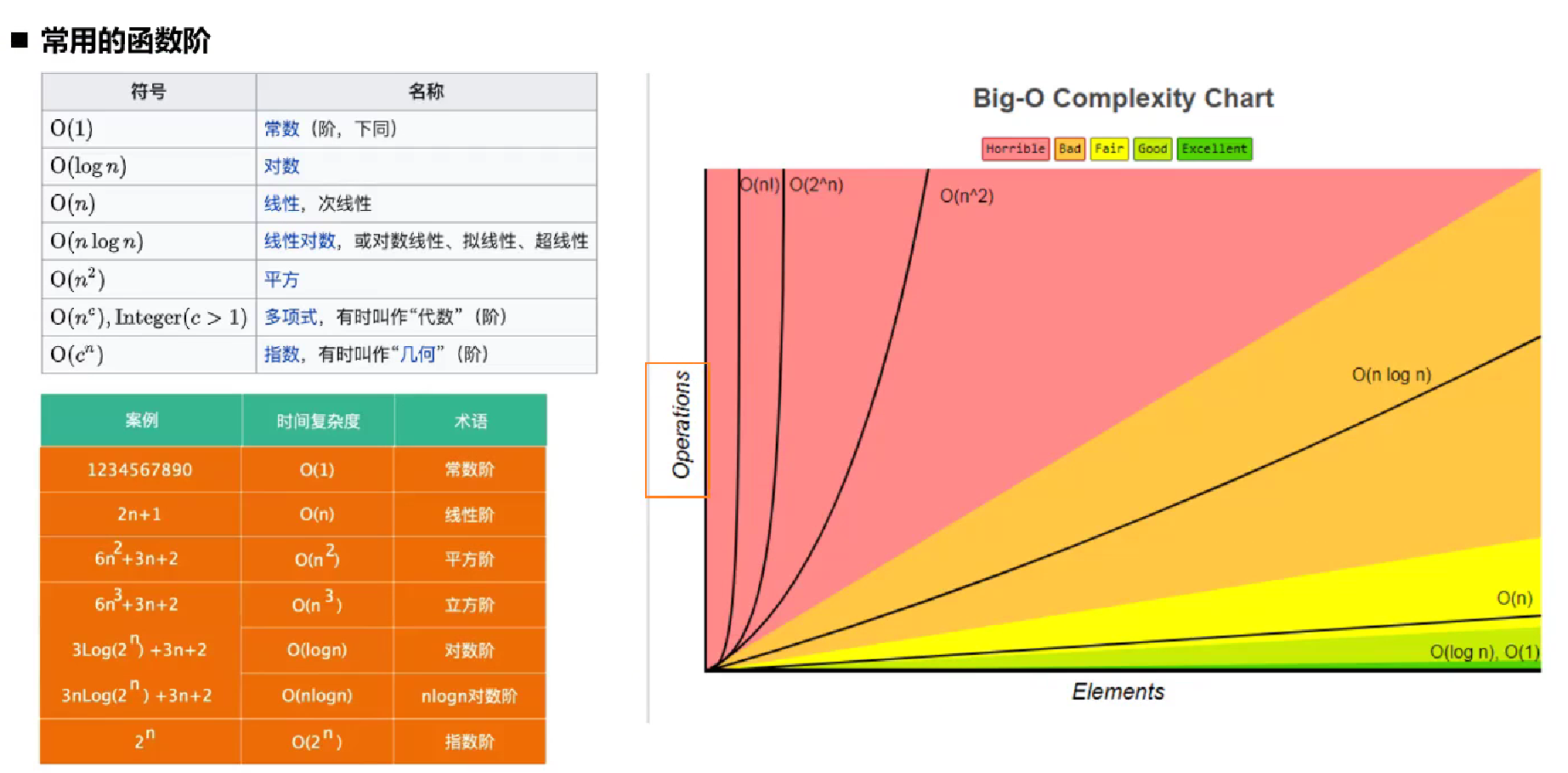
基础
先进后出
受限的线性结构
栈结构实现
基于数组
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 import IStack from "./type" ;class ArrayStack <T = any > implements IStack <T> {private data : T[] = [];push (element : T): void {this .data .push (element);pop (): T | undefined {return this .data .pop ()peek (): T | undefined {return this .data [this .data .length - 1 ]isEmpty (): boolean {return this .data .length === 0 size (): number {return this .data .length export default ArrayStack
基于链表
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 import ArrayStack from "./stack" ;import Stack from "./stack" ;function decimalToBinary (decimal: number ): string {const stack = new ArrayStack <number >()while (decimal > 0 ) {const result = decimal % 2 push (result)Math .floor (decimal / 2 )while (!stack.isEmpty ()) {console .log (stack.pop ())return '' decimalToBinary (35 )export {}
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 import ArrayStack from "./stack" ;function isValid (s: string ): boolean {const stack = new ArrayStack ()for (let i = 0 ; i<s.length ; i++){const c = s[i]if (c === '(' ) {push (')' )else if (c === '[' ) {push (']' )else if (c === '{' ) {push ('}' )else {if ( c !== stack.pop () ) return false return stack.isEmpty ()console .log (isValid ("()" ))console .log (isValid ("()[]{}" ))console .log (isValid ("(]" ))
基础
先进先出
受限的线性结构
实现
基于数组
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class ArrayQueue <T> {private data : T[] = []enqueue (element : T): void {this .data .push (element)dequeue (): T | undefined {return this .data .shift ()peek (): T | undefined {return this .data [0 ]isEmpty (): boolean {return this .data .length === 0 size (): number {return this .data .length get size (): number {return this .data .length const queue = new ArrayQueue <string >()
基于链表
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 import ArrayQueue from "./queue" ;function hotPotato (names: any [], num: number ) {const queue = new ArrayQueue <string >()for (const name of names) {enqueue (name)while (queue.size () > 1 ) {for (let i = 0 ; i < num; i++) {const name = queue.dequeue ()if (name) {enqueue (name)dequeue ()return queue.dequeue ()const lastName = hotPotato (["John" , "Tom" , "Mary" ,"Bob" , "abs" , "nsd" , "qswd" ], 4 )console .log (lastName)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 import ArrayQueue from "./queue" ;function lastRemaining (n: number , m: number ) {const queue = new ArrayQueue <number >()for (let i = 0 ; i < n; i++) queue.enqueue (i)while (queue.size () > 1 ) {for (let i = 1 ; i < m; i++) {enqueue (queue.dequeue ()!)dequeue ()return queue.dequeue ()!console .log (lastRemaining (10 ,17 ))const result = lastRemaining (5 ,3 )console .log (result)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 class Node <T> {value : Tnext : Node <T> | null = null ;constructor (value: T ) {this .value = valueclass LinkList <T> {head : Node <T> | null = null ;private size : number = 0 ;get length () {return this .size private getNode (position : number ): Node <T> | null {let current = this .head let index = 0 while (index++ < position && current) {next return currentappend (value: T ) {const newNode = new Node (value);if (!this .head ) {this .head = newNodeelse {let current = this .head while (current.next ) {next next = newNodethis .size ++traverse (const values : T[] = []let current = this .head while (current) {push (current.value )next console .log (values.join ("->" ))insert (value: T, position: number ) {if (position < 0 || position > this .size ) return false const newNode = new Node <T>(value)if (position === 0 ) {next = this .head this .head = newNodeelse {let previous = this .getNode (position - 1 )next = previous!.next next = newNodethis .size ++removeAt (position : number ): T | null {if (position < 0 || position >= this .size ) return null let current = this .head if (position === 0 ) {if (this .head === null ) return null this .head = current?.next ?? null else {let previous = this .getNode (position -1 )next = previous?.next ?.next ?? null this .size --return current?.value ?? null get (position : number ): T | null {if (position < 0 || position >= this .size ) return null return this .getNode (position)?.value ?? null update (value: T, position: number ) {if (position < 0 || position >= this .size ) return false let current = this .getNode (position)value = valuereturn true indexOf (value : T): number {let current = this .head let index = 0 while (current) {if (current.value === value) {return indexnext return -1 remove (value : T): T | null {let index = this .indexOf (value)return this .removeAt (index)isEmpty ():boolean {return this .size === 0 export {}
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 `` ` ## 删除链表中的节点 ` `` typescriptvar deleteNode = function (node ) {val = node.next .val next = node.next .next
非递归998
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 function reverseList (head: ListNode | null ): ListNode | null {if (head === null || head.next === null ) return headlet newHead : ListNode | null = null while (head) {const current = head.next next = newHeadreturn newHead
递归999
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 function reverseList (head: ListNode | null ): ListNode | null {if (head === null || head.next === null ) return headconst newHead = reverseList (head?.next || null )next .next = headnext = null return newHead
基于数组进行实现
解决冲突
链地址法
重复数据采取链表方式进行存储
开放地址法
寻找空白单元来添加重复数据
装填因子 = 总数 / 地址数,越大效率越低;大于0.75扩容
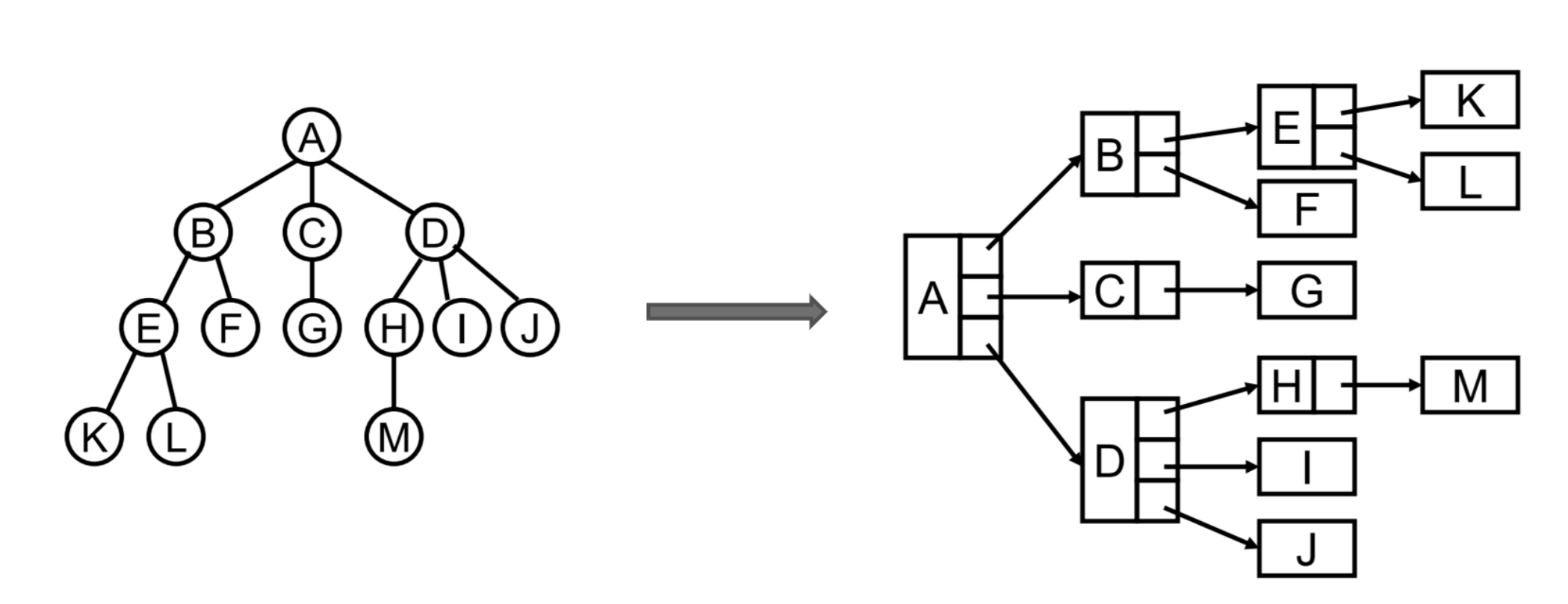
树是由n个节点构成的有限集合
image-20230701164134165
每个树节点都最多只有两个节点
一棵二叉树第i曾的最大节点数为 2 ^ (n-1)
深度为k的二叉树有最大节点总数为2^k -1
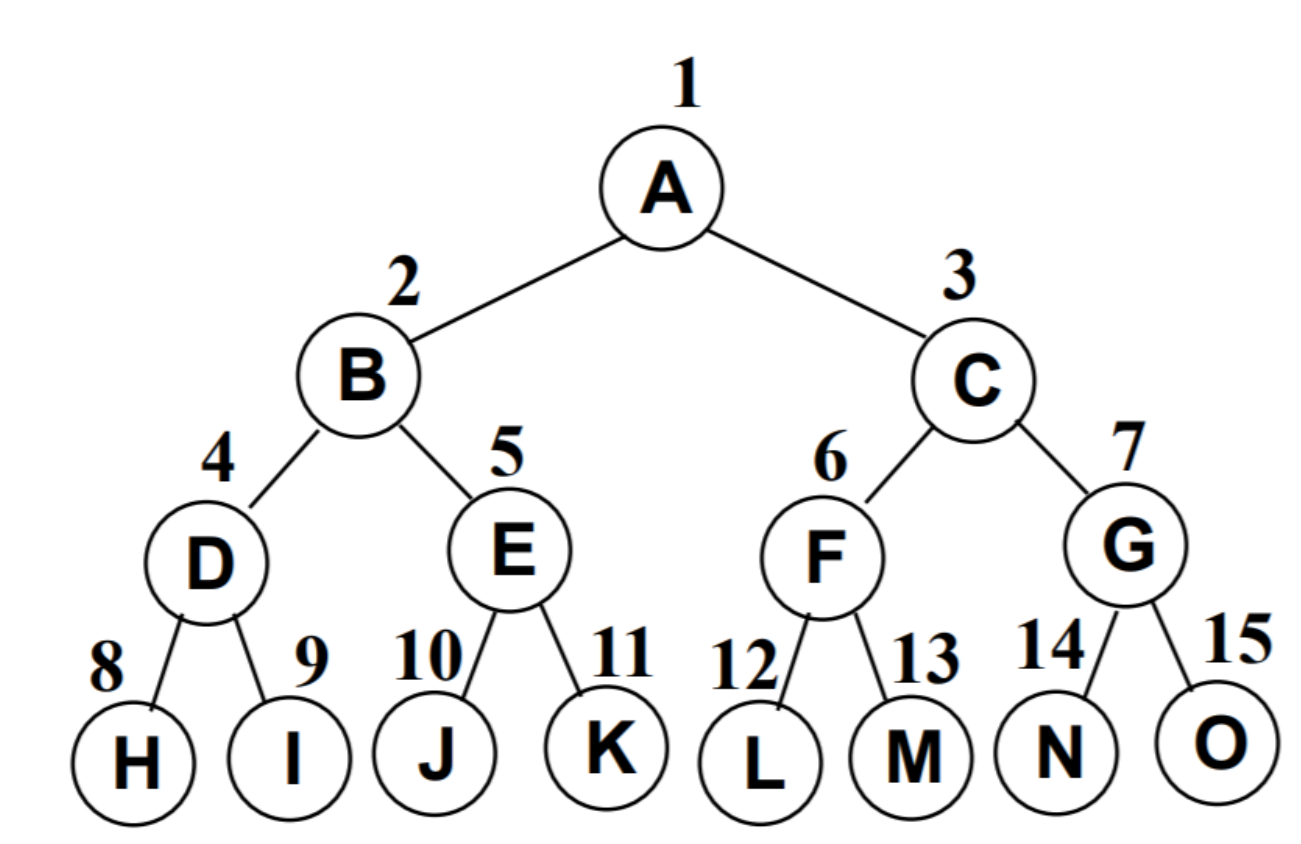
在二叉树中,除了最下一层的叶子节点外,每层节点都是2个子节点,就构成满二叉树
除二叉树最后一层外,其他各层的节点数都达到最大个数
最后一层从左向右的叶子节点连续存在,只缺右侧若干节点
完美二叉树是特殊的完全二叉树
非空左子树的所有键值小于根节点的键值
非空右子树的所有键值大于根节点的键值
左右子树本身也是二叉搜索树
封装节点
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 class BSTNode <T> {value : Tright : Node <T> | null left : Node <T> | null class BSTree <T> {root : Node <T>
常见操作
插入操作:
insert(value):向树中插入一个新的数据。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 insert (value: T ) {const newNode = new Node (value)if (!this .root ) {this .root = newNodeelse { this .insertNode (this .root , newNode)private insertNode (node:Node<T>, newNode: Node<T> ) {if (node.value > newNode.value ) { if (!node.left ) {left = newNodeelse {this .insertNode (node.left , newNode)else { if (!node.right ) {right = newNodeelse {this .insertNode (node.right , newNode)
查找操作:
search(value):在树中查找一个数据,如果节点存在,则返回true;如果不存在,则返回false。
min:返回树中最小的值/数据。
max:返回树中最大的值/数据。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 search (value : T): boolean {return this .searchNode (this .root , value)private searchNode (node : Node <T> | null , value : T): boolean {if (node === null ) return false if (node.value > value) {return this .searchNode (node.left , value)else if (node.value < value) {return this .searchNode (node.right , value)else {return true
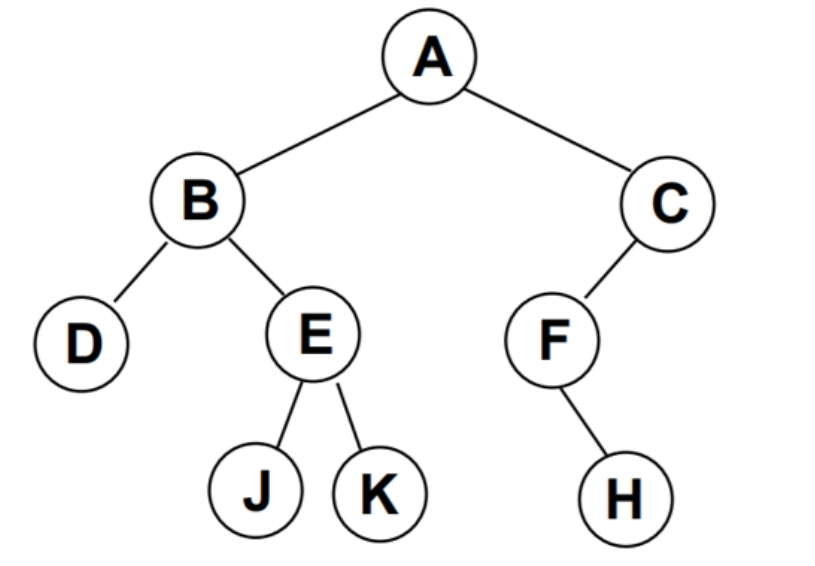
遍历操作:
inOrderTraverse:通过中序遍历方式遍历所有节点。
preOrderTraverse:通过先序遍历方式遍历所有节点。
postOrderTraverse:通过后序遍历方式遍历所有节点。
levelOrderTraverse:通过层序遍历方式遍历所有节点。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 preOrderTraverse (node: Node<T> | null = null ) {this .preOrderTraverseNode (node)private preOrderTraverseNode (node: Node<T> | null = null ) {if (node) {this .preOrderTraverseNode (node.left )console .log (node.value )this .preOrderTraverseNode (node.right )inOrderTraverse (node: Node<T> ) {this .inOrderTraverseNode (node)private inOrderTraverseNode (node: Node<T> | null = null ){if (node) {console .log (node.value )this .inOrderTraverseNode (node.left )this .inOrderTraverseNode (node.right )postOrderTraverse (node: Node<T> | null = null ) {this .postOrderTraverseNode (node)private postOrderTraverseNode (node: Node<T> | null = null ) {if (node) {this .postOrderTraverseNode (node.right )this .postOrderTraverseNode (node.left )console .log (node.value )levelOrderTraverse (this .levelOrderTraverseNode ()private levelOrderTraverseNode (if (!this .root ) return const queue : Node <T>[] = []push (this .root )while (queue.length ) {const current = queue.shift ()!console .log (current.value )if (current.left ) {push (current.left )if (current.right ) {push (current.right )
删除操作(有一点点复杂):
remove(value):从树中移除某个数据。
考虑当前被删除节点是否有子节点,子节点是一个还是两个
优势
可以快速地找到给定关键字的数据项 并且可以快速地插入和删除数据项。
如果插入的数据是有顺序的很可能会变成链表,树非常的不平衡不均匀。
为保证树的查找效率,所以我们在一定程度上需要树保持平衡。
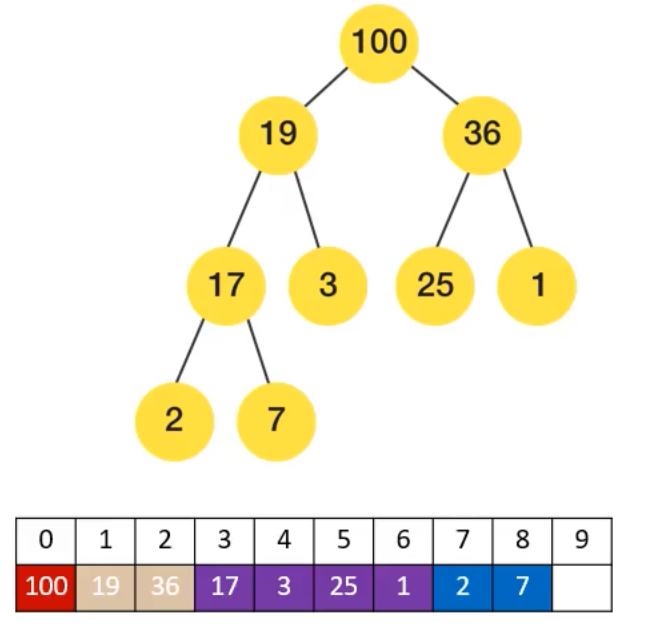
完全二叉树,分最大堆和最小堆
image-20230630101635814
时间复杂度
image-20230626105233684
空间复杂度
数组有序
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 function binarySearch (array: number [], num: number ): number {let left = 0 let right = array.length - 1 while (left <=right) {let mid = Math .floor ((left + right) / 2 )let minNum = array[mid]if (minNum === num) {return midelse if (minNum > num) {1 else {1 return -1 export {}
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 function getRandomNumber (min1, max1 ) {let min = Math .ceil (min1)let max = Math .floor (max1)return Math .floor (Math .random () * (max - min + 1 ) + min)let initArr = Array .from ({ length : 10 }, () => { return getRandomNumber (0 , 99 ) });new Set (initArr)];sort ((a, b ) => a - b);const map = {}forEach (item =>let key = Math .floor (item / 10 )if (!map[key]) {push (item)const result = []for (const key in map) {push (map[key])console .log (result)
// 方法一:递归
// 每次处理一层结构,通过判断属性的值是否是对象来确定递归是否结束
// - 如果是对象,则表示递归没有结束,递归调用
// - 如果不是对象,表示递归的最后一层,确定属性值
// 方法二:while循环-队列
// 使用Object.entries()方法,处理原始对象
// 使用队列存储每一层的值,知道队列中的值处理完毕
# 摩尔投票法